About era 1960 – 1969

The Sixties and the space age. Successfully performing manned space missions were the biggest challenge imaginable.

By AWCo on 8 July 2019
During World War II the United States and the Soviet Union fought together as allies against the German occupation. When this war came to an end, Europe was divided by the hands of the capitalist USA and Joseph Stalin’s communist government. This division happened at the end of the war but at the same time it started a new one; the cold war.
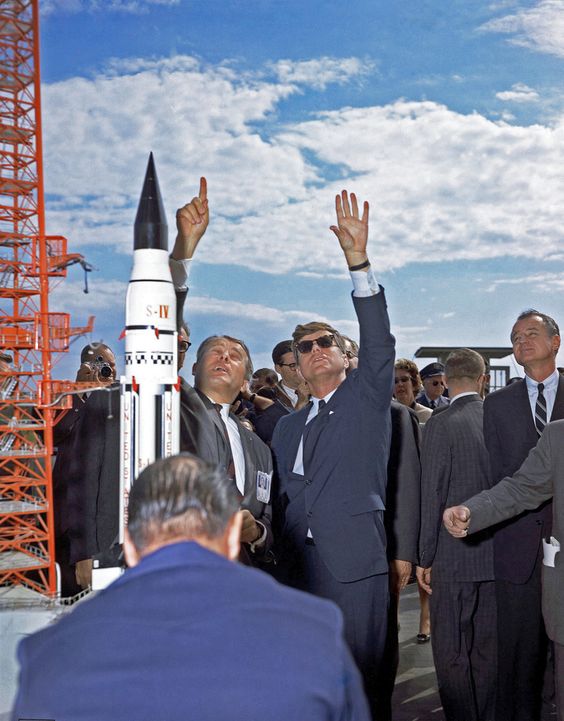

The start of 'Space Age'
What started off as a cultural leadership difference escalated quickly into a competition of what country was the ‘greatest’. In the 1950s the development of atomic weapons was the primary goal for both countries and when they knew they had both developed bombs they would never want to use, the focus of the cold war shifted towards space. The outer space was still unknown territory and at that time, successfully performing manned space missions was the biggest challenge imaginable, and so the ‘Space Race’ started.
"First, I believe that this nation should commit itself to achieve the goal, before this decade is out, of landing a man on the moon and returning him safely to the Earth." - John F. Kennedy, 1961.
It was not just these two counties who developed quickly, the whole world was on a fast track towards modernization. Pan-American airways were investing big money to make air travel available for a wider public. The velocity in motorsport was higher than ever before, and the pace with which the Swiss watch manufacturers developed wristwatches was incredible. Their biggest achievement in this decade? An automatic chronograph movement, seen first on the market in the beloved Heuer Autavia in 1969.
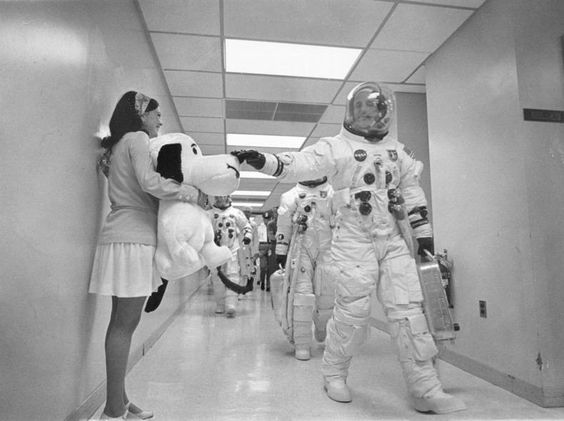

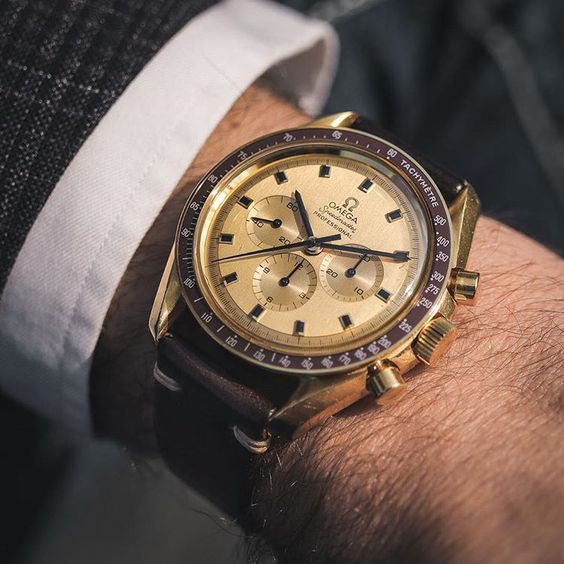
Mankind’s need for speed asked for more and more precision watches for timed measurements and navigation. Imagine a 1960s space shuttle losing its navigation instruments when in outer space, guess how you’d know where you were or where you needed to go? Well, you would never be entirely sure but a chronograph wristwatch was the most helpful tool to astronauts in such a situation. That’s why NASA made a chronograph watch a part of the standard equipment for astronauts.
After comparing many chronographs from different Swiss watch houses, and putting them through a variety of test under challenging conditions, the Omega Speedmaster was the chosen one. Under extreme conditions, the Speedmaster performed best and was the watch to come along on the Apollo 11, NASA’s space mission to the moon. It was this mission that ended the space race on July 24, 1969, when Neil Armstrong, Edwin ‘Buzz’ Aldrin, and Michael Collins returned from their walk on the moon. The USA won the space race and the Omega Speedmaster became the Moonwatch which we’ll never stop admiring.